Nov 11, 2021 | Brazil, Economics, Environment
By Fanni Daniella Szakal, 2021 IIASA Science Communication Fellow
In an attempt to foster economic development for Brazil, the government is planning to open up indigenous and protected areas for mining. But will this truly lead to economic development for the country? 2021 Young Scientists Summer Program (YSSP) participant, Sebastian Luckeneder is using spatial modeling to find out.
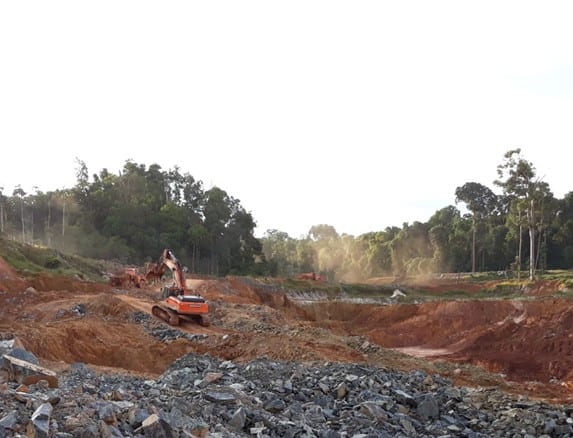

© Prabhash Dutta | Dreamstime.com
As the largest rainforest on the planet, the Amazon harbors the highest biodiversity of all ecosystems and is home to many indigenous tribes. It is also literally sitting on a goldmine of natural resources. There are plans in the works to open up protected and indigenous areas of the rainforest to mining activities, which is expected to bring more wealth and development for the country, but at the same time, it will also pose a threat to the environment and indigenous communities.
At first glance, the issue looks like the classic trade-off between economic growth versus environmental and social disruption. In reality however, mining affects social, environmental, and economic spheres both directly and indirectly, creating a complex network of interactions that potentially defy the current dogma.
Mining relies heavily on machines while creating relatively few jobs in comparison to the investment of capital it requires. In addition, mining companies are often large international corporations, which means that most of the profits gained from mining operations in a particular country end up outside that country’s borders.
“One could say that just the very few benefit from extractive activities, whereas many have to pay the cost,” says Sebastian Luckeneder, a 2021 YSSP participant at IIASA, when referring to the environmental destruction, disruption of livelihoods, and displacement of indigenous communities that mining would bring about.
As a second-year PhD candidate at the Institute for Ecological Economics of Vienna University of Economics and Business (WU), Luckeneder is studying the environmental and socioeconomic impacts of mining activities. At IIASA, he used spatial modeling to understand how mining and land use affect regional economic growth in Brazil in the hopes of finding the best economic solution for the country.
Using GDP growth as a proxy for economic development, he looked at the impacts of mining and other types of land use between 2000 and 2020. The model incorporates data on mining, agriculture, and land-use change, as well as other socioeconomic factors, such as employment and infrastructure for about 5,500 municipalities in Brazil.
The study is as complex as it sounds: Luckeneder’s main challenge is to set up a theoretical framework that depicts how the environmental and socioeconomic factors influence each other. Once his comprehensive model is complete, he hopes to get a clear picture of how mining affects the Brazilian economy.
He suspects that while mining activities would bring some economic gains, these might not be sustainable, as the environmental and social upheaval that follow the opening of a mine could negatively impact development in the long-run.
While economic development is important, in the current climate crisis, decisions to enable activities that lead to deforestation cannot be taken lightly. Luckeneder hopes that his results will be used to inform the political debate in Brazil and support policy decisions by the way of science.
Sep 23, 2021 | Brazil, China, Data and Methods, Energy & Climate, India, Russia, Science and Policy, Young Scientists
By Neema Tavakolian, 2021 IIASA Science Communication Fellow
Ever wonder why countries can never agree on issues related to climate change and the environment? Young Scientists Summer Program (YSSP) participant Felix Schenuit dives into the politics and challenges surrounding carbon dioxide removal in international climate negotiations.
The Paris Agreement has been lauded as a landmark effort to address climate change and has been signed by nearly every country in the world. The agreement sets out ambitious goals such as reaching temperature targets, setting net-zero carbon targets, and providing financial, technical, and capacity building support to those countries that need it.
One topic that has been receiving increasing attention since the adoption of the agreement is carbon dioxide removal, or CDR – which comprises man made processes involving the direct removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and sequestering it somewhere else, usually underground or under the sea floor. Since it was first proposed, CDR has been discussed on many platforms including critical comments, journals, and studies. 2021 IIASA YSSP participant Felix Schenuit studies how the debate, which has been largely ignored by policymakers until the Paris Agreement, is evolving, and how CDR is being taken up in climate policymaking.

© Felix Schenuit
Felix Schenuit comes from a background of political science and public policy. It was during his employment at the German Institute for International and Security Affairs (SWP) that he became fascinated by CDR and the political debates surrounding the impacts it can have on the fight against climate change. This is when he decided to combine his newfound interest with his background and experiences in international relations and public policy to pursue a PhD at the University of Hamburg comparing CDR policymaking in different countries and the role scientific knowledge has on its implementation.
Building on a previous study comparing CDR governance among nine Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) cases, Schenuit is now focusing on the role of scientific knowledge surrounding CDR in Brazil, China, India, and Russia. These countries account for a significant portion of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions due to their rapid industrialization and expanding economies. China and India are especially significant due to their great influence in ongoing international climate negotiations regarding the Paris Agreement.
Schenuit uses integrated assessment models to gather information and data about the role of CDR in different countries in decarbonization pathways.
“These models help us to understand what amount of CDR we are likely to need to achieve Paris Agreement targets. Case studies on specific countries are an important second step to explore facts on the ground about different policy initiatives, emerging CDR facilities, and efforts in each region. We reach out to country experts and build interdisciplinary bridges to investigate how CDR is addressed politically, what amounts are available and politically feasible, as well as relevant knowledge gaps,” he explains.
One of the biggest challenges remaining for CDR is limited knowledge about different CDR methods, both in science and policy circles. There are many ways one can remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, ranging from afforestation, to soil carbon sequestration, ocean fertilization, direct CO2 capture from the air, and the use of biochar, among others.

Reforestation on hill at Bao Loc mountain pass, Vietnam © Hoxuanhuong | Dreamstime.com
“When it comes to methods, many policymakers are unaware of the portfolio of available methods. Each method has different tradeoffs, both environmentally and politically. For example, in Germany, carbon capture and storage (CCS) is very contested and most policymakers are hesitant to even address CDR. Thus, in Germany one may need a different set of methods than in the UK, for example, where CCS-based CDR methods are pursued proactively,” Schenuit says.
Many predict that the role of international politics in CDR governance under the Paris Agreement is going to be difficult and tricky to navigate. Schenuit argues that it is still a bit too early in the debate for predictions as policymakers have only recently been directly addressing CDR. He does however agree that there is already strong evidence of politics at play and alliances are forming.
The study on Brazil, China, India, and Russia will yield fascinating results, as it will give us an idea about future disputes and questions regarding the carbon in our atmosphere. Questions like where we will be removing carbon and who is going to pay for it. One thing is for certain, however. Time is running out to meet the targets of the Paris Agreement, and international cooperation is desperately needed.
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the Nexus blog, nor of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.
Aug 12, 2021 | Climate Change, Evolution, Science and Policy, Women in Science, Young Scientists
By Neema Tavakolian, 2021 IIASA Science Communication Fellow
Young Scientists Summer Program (YSSP) participant Lyndsie Wszola explores how human interactions with warming freshwater systems have affected the evolution of fish species through the lens of the North American walleye.

© Justinhoffmanoutdoors | Dreamstime.com
The effects of climate change have intensified over the past few years, especially in our oceans, and human based activities contributing to it are now being taken more seriously. While the warming of our oceans is indeed troubling, many forget that freshwater systems are also being influenced, and that this is affecting the growth and evolution of the species that reside in them.
2021 YSSP participant Lyndsie Wszola wants to explore changes in freshwater systems using human-natural modeling systems at IIASA.

© Lyndsie Wszola
Growing up with a conservation officer father, Wszola is a second-generation conservationist. Knowing she wanted to enter this field at an early age, she realized that she had to get into research and academia first. Her main interests while studying at the University of Nebraska have been the interactions between humans and wildlife.
While researching the relationships between hunters and ring-necked pheasants, she discovered an affinity for quantitative research. This curiosity went even further after she discovered literature on harvest induced evolution and mathematical ecology specifically pertaining to fish populations. Together, this initial desire to explore human and wildlife interactions and her newfound interest in mathematical ecology, led Wszola to take a closer look at North American freshwater systems and how we as humans are influencing its ecology. Her research specifically delves into the growth and evolutionary changes seen in the North American walleye (Sander vitreus) – a popular fish in Canada and the United States. The reason for its fame is its palatable taste as a freshwater fish and its status among anglers, making it both a commercially and recreationally fished species.
Walleye was chosen as the subject of Wszola’s research for many reasons. First, walleye, like many fish, are ectotherms meaning that their body processes and behaviors are directly linked to their body temperature, which is in turn directly linked to the temperature of the water. Unlike other fish however, there is already plenty of research and data on the relationship between the walleye’s growth and temperature. This information makes it much easier to simulate the walleye’s eco-evolutionary growth dynamics in the context of human driven harvests in warming waters. Wszola will also be working with very large datasets spanning multiple latitudes ranging from Ontario, Canada down to Nebraska, USA. The datasets include up to six million fish with four million of those being walleye.
“My goal is to model the influence of temperature on fish harvests based on size. Due to their ectotherm nature, we can observe the changes in body size in annual harvests. As waters warm, walleye grow much faster. We also know that intensely harvested fish often evolve to reach maturation at smaller sizes. When coupled with rising temperatures, this relationship between harvest induced and temperature induced evolution can be fascinating, as we now have two sources working together to change the growth evolution of this fish,” she explains.
Due to warming temperatures, many natural resources are at stake with some of the most sensitive being aquatic in nature. Research like this is important as it allows us to look at our relationships with the environment to be able to react accordingly.
“I hope that the research I do yields fascinating enough results so that from a practical standpoint, future fisheries policies can include climate change dynamics in addition to fish and human dynamics,” Wszola concludes.
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the Nexus blog, nor of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.
Jul 29, 2021 | Korea, Science and Policy, Young Scientists
By Fanni Daniella Szakal, 2021 IIASA Science Communication Fellow
Despite the political challenges, 2021 YSSP participant Eunbeen Park is researching ways to restore forests in isolated North Korea.

© Znm | Dreamstime.com
North Korea is somewhat of an enigma and getting a glimpse into what transpires behind its borders is a difficult task. Based on our limited information, it however seems that its once luscious forests have disappeared at an alarming rate in the last few decades.
Deforestation in North Korea is fueled by economic difficulties, climate change, and a lack of information for effective forest management. As forests are recognized as important carbon sinks that are invaluable when working towards the climate goals established in the Paris Agreement, finding a way to restore them is imperative. Forests are also essential in solving food insecurity and energy issues, which is especially relevant in the face of the current economic hardship in North Korea.
Neighboring South Korea serves as a benchmark for a successful reforestation campaign after having restored most of its forest cover in the last half a century. South Korean researchers and NGOs are keen to support afforestation efforts in North Korea and it seems that the North Korean government is also prioritizing this through a 10-year plan announced by North Korean leader Kim Jong-Un in 2015. The strained relationship between the two Koreas however, often hinders effective collaboration.
‘’We are close to North Korea regionally, but direct connection is difficult for political reasons. However, many researchers are interested in studying North Korea and there are currently many projects for South and North Korea collaboration supported by the Ministry of Unification,” says Eunbeen Park, a participant in the 2021 Young Scientists Summer Program and a second year PhD student in Environmental Planning and Landscape Architecture at Korea University in Seoul, South Korea.

North Korean countryside © Znm|Dreamstime.com
Modeling afforestation scenarios in North Korea
Park specializes in using remote sensing data for environmental monitoring and detecting changes in land cover. During her time at IIASA, she will use the Agriculture, Forestry, and Ecosystem Services Land Modeling System (AFE-LMS) developed by IIASA to support forest restoration in North Korea.
First, Park will use land cover maps dating back to the 1980s to map the change in forest cover. She will then identify areas for potential afforestation considering land cover change, forest productivity, climate, and different environmental variables, such as soil type. She will also develop different afforestation scenarios based on forest management options and the tree species used.
According to Andrey Krasovskiy, Park’s supervisor at IIASA, when selecting tree species for afforestation we need to take into account their economic, environmental, and recreational values.
“From a set of around 10 species we need to choose those that would be the most suitable in terms of resilience to climate change and to disturbances such as fire and beetles,” he says.
Challenges in data collection
A major challenge in Park’s research is obtaining accurate information for building her models. If there is relevant research from North Korea, it is not available to foreign researchers and without being able to enter the country to collect field data in person, her research has to rely on remote sensing data or data extrapolated from South Korean studies.
Fortunately, in recent years, remote sensing technology has evolved to provide high-resolution satellite data through which we are able to take a thorough look at the land cover of the elusive country. Park will match these maps with yield tables provided by Korea University based on South Korean data. As the ecology of the two Koreas are largely similar, these maps are thought to provide accurate results.
Is there space for science diplomacy?
“Research shouldn’t have any boundaries,” notes Krasovskiy. “In reality however, the lack of scientific collaboration between research groups in South and North Korea poses a major obstacle in turning this research into policy. Luckily, some organizations, such as the Hanns Seidel Foundation in South Korea, are able to bridge the gap and organize joint activities that provide hope for a more collaborative future.”
Despite the diplomatic hurdles, Park hopes that her work will find its way to North Korean policymakers.
“I expect my research might make a contribution to help policymakers and scientific officials establish forest relevant action in North Korea,” she concludes.
May 20, 2021 | COVID19, Poverty & Equity, Risk and resilience, Women in Science
By Benigna Boza-Kiss, Shonali Pachauri, and Caroline Zimm from the IIASA Transformative Institutional and Social Solutions Research Group
Benigna Boza-Kiss, Shonali Pachauri, and Caroline Zimm explain how COVID-19 has impacted the poor in cities and what can be done to increase the future resilience of vulnerable populations.

© Manoej Paateel | Dreamstime.com
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a halt to life as we knew it. We have been restrained in our activities and freedoms, forced to stay indoors at home, to cancel travel plans, and to transfer meetings to an online space, where most of us have also celebrated birthdays and other important life events that should have been in person with our loved ones. These changes have impacted many aspects of our comfort, our social wellbeing, as well as our financial situations, but it has also brought existing inequalities and poverty into the spotlight.
The risks of the pandemic and restrictions following containment measures have been felt most acutely by the poor, the vulnerable, those in the informal sector, and those without savings and safety nets. The suffering of women in the health sector, school children in households without electricity and internet, workers in the informal sector that don’t have the option to telework, crowds living in slums – to name just a few examples of vulnerable groups – have become glaringly visible to all. These people have had to adapt to new rules and conditions when they were living on the edge even before the pandemic.
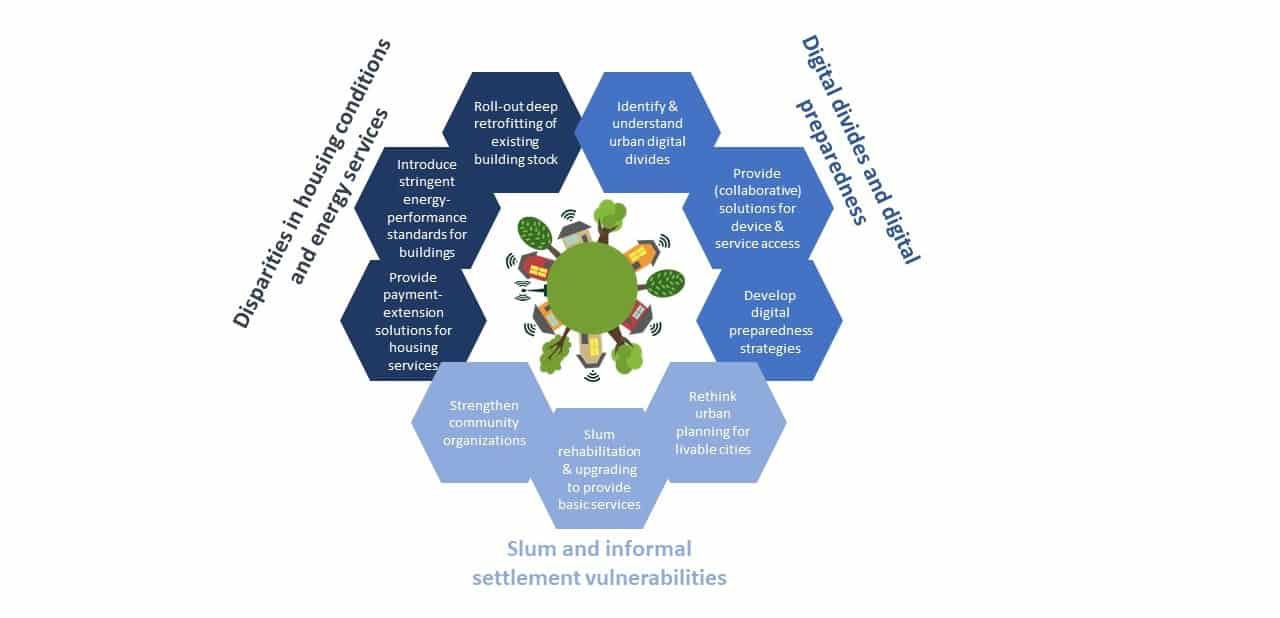
In a new perspective piece published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Cities, we explored how aspects related to access to shelter/housing, modern energy, and digital services in cities have influenced the poor and what can be done to increase the future resilience of vulnerable populations.
We described three ways in which the COVID-19 pandemic and related containment measures have exacerbated urban inequalities, and identified how subsequent recovery measures and policy responses could redress these.
First, lockdowns amplified urban energy poverty. Staying at home has meant increased energy use at home. For the poor, who already struggle with utility costs, and typically live in low energy quality buildings, these services have become even more unaffordable. These populations also shoulder a higher burden of poor health, for example, higher incidence of respiratory problems, with poor or inadequate ventilation and insulation increasing their risk of infection even more.
Second, preexisting digital divides have surfaced, even within well-connected cities. Multiple barriers limit digital inclusion: access to digital technologies due to high costs (for devices, internet access, and electricity connections), and unreliable services (again both for electricity and internet), as well as low digital literacy and support. This lack of adequate digital service access is contributing to these populations falling further behind during lockdowns as they miss out on education and income.
Third, slum dwellers in the world’s cities have been particularly hard hit, because of precarious and overcrowded housing conditions, lack of basic infrastructure and amenities, and a high concentration of the socioeconomically disadvantaged, resulting in even more negative consequences of lockdown measures. With many slum inhabitants working in the informal sector, many have been left either without jobs and income, or have been compelled to work in precarious and unsafe conditions to survive. The loss of income has also had knock-on effects, making payments of regular expenditures for rent, water, electricity, and other utility services difficult. Women within these settlements have been disproportionately impacted by the pandemic, as they are over represented in the informal economy, and more likely to be engaged in invisible work, such as home-based or domestic and care work.
Recovery measures need to ensure immediate relief, but also point towards long-term solutions that contribute to the redistribution of wealth and new urban development, while also increasing resilience to the current and future pandemics or other disasters. There are tested measures that should be reemphasized.
Urban green recovery plans that include large-scale home renovation programs could ensure warm, healthy homes, and affordable energy bills for all. In the shorter-term, alleviation of payment defaults on the rents and utility bills of the energy poor should continue. In parallel, urban digital preparedness, more equal access to the virtual delivery of essential services, and provision of opportunities for virtual working and education for all in the future, need attention.
COVID-19 can be a wake up call to increase efforts to close the digital divide and push for structural change. The crisis has increased the urgency to redesign and improve informal settlements and provide adequate and efficient services that address the diverse needs of poor urban residents. This requires partnerships between urban municipalities, planners, and stakeholders, as well as strengthening local communities for inclusive planning strategies. More immediately, it is necessary to provide direct support to slum and informal settlement populations in terms of income support, adequate nutrition, energy, water, and other basic infrastructure and services.
 All in all, the COVID-19 pandemic has been a “test of societies, of governments, of communities, and of individuals”. Digital technologies, home renovation, and slum rehabilitation are the means, rather than the end to improve conditions for all, but if specifically targeted to the poor and most deprived, such measures can reduce inequalities and increase resilience.
All in all, the COVID-19 pandemic has been a “test of societies, of governments, of communities, and of individuals”. Digital technologies, home renovation, and slum rehabilitation are the means, rather than the end to improve conditions for all, but if specifically targeted to the poor and most deprived, such measures can reduce inequalities and increase resilience.
Reference:
Boza-Kiss, B., Pachauri, S., & Zimm, C. (2021). Deprivations and Inequities in Cities Viewed Through a Pandemic Lens. Frontiers in Sustainable Cities 3 e645914. [pure.iiasa.ac.at/17121]
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the Nexus blog, nor of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.










You must be logged in to post a comment.