By Benigna Boza-Kiss, Shonali Pachauri, and Caroline Zimm from the IIASA Transformative Institutional and Social Solutions Research Group
Benigna Boza-Kiss, Shonali Pachauri, and Caroline Zimm explain how COVID-19 has impacted the poor in cities and what can be done to increase the future resilience of vulnerable populations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a halt to life as we knew it. We have been restrained in our activities and freedoms, forced to stay indoors at home, to cancel travel plans, and to transfer meetings to an online space, where most of us have also celebrated birthdays and other important life events that should have been in person with our loved ones. These changes have impacted many aspects of our comfort, our social wellbeing, as well as our financial situations, but it has also brought existing inequalities and poverty into the spotlight.
The risks of the pandemic and restrictions following containment measures have been felt most acutely by the poor, the vulnerable, those in the informal sector, and those without savings and safety nets. The suffering of women in the health sector, school children in households without electricity and internet, workers in the informal sector that don’t have the option to telework, crowds living in slums – to name just a few examples of vulnerable groups – have become glaringly visible to all. These people have had to adapt to new rules and conditions when they were living on the edge even before the pandemic.
In a new perspective piece published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Cities, we explored how aspects related to access to shelter/housing, modern energy, and digital services in cities have influenced the poor and what can be done to increase the future resilience of vulnerable populations.
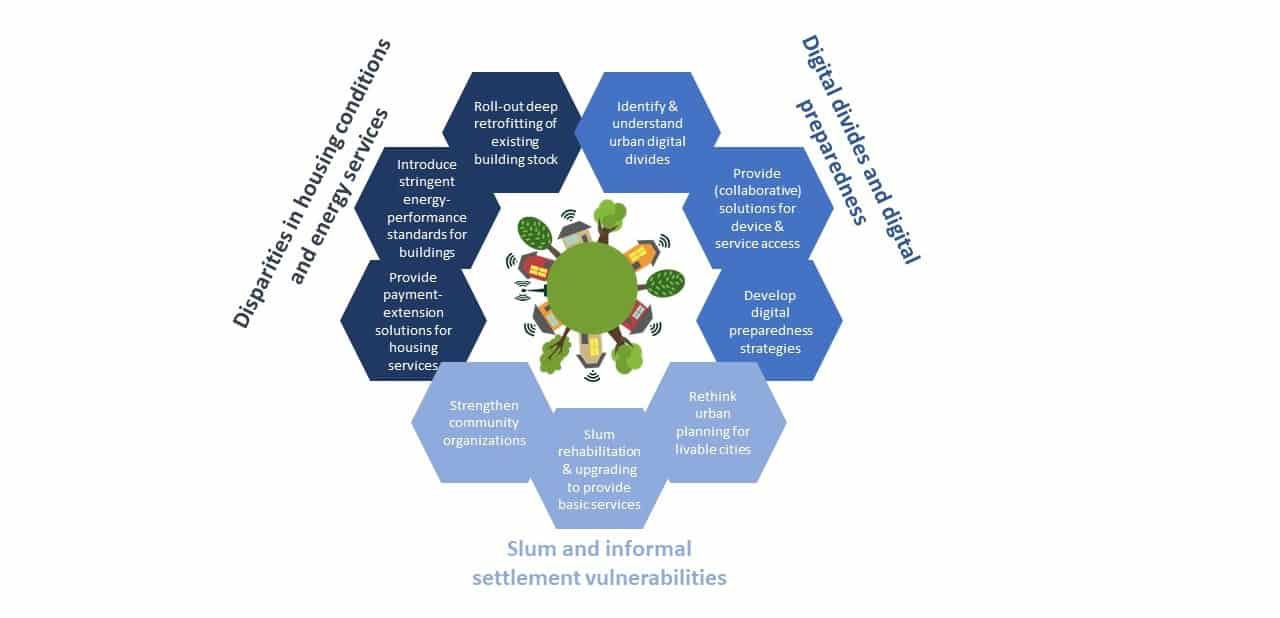
We described three ways in which the COVID-19 pandemic and related containment measures have exacerbated urban inequalities, and identified how subsequent recovery measures and policy responses could redress these.
First, lockdowns amplified urban energy poverty. Staying at home has meant increased energy use at home. For the poor, who already struggle with utility costs, and typically live in low energy quality buildings, these services have become even more unaffordable. These populations also shoulder a higher burden of poor health, for example, higher incidence of respiratory problems, with poor or inadequate ventilation and insulation increasing their risk of infection even more.
Second, preexisting digital divides have surfaced, even within well-connected cities. Multiple barriers limit digital inclusion: access to digital technologies due to high costs (for devices, internet access, and electricity connections), and unreliable services (again both for electricity and internet), as well as low digital literacy and support. This lack of adequate digital service access is contributing to these populations falling further behind during lockdowns as they miss out on education and income.
Third, slum dwellers in the world’s cities have been particularly hard hit, because of precarious and overcrowded housing conditions, lack of basic infrastructure and amenities, and a high concentration of the socioeconomically disadvantaged, resulting in even more negative consequences of lockdown measures. With many slum inhabitants working in the informal sector, many have been left either without jobs and income, or have been compelled to work in precarious and unsafe conditions to survive. The loss of income has also had knock-on effects, making payments of regular expenditures for rent, water, electricity, and other utility services difficult. Women within these settlements have been disproportionately impacted by the pandemic, as they are over represented in the informal economy, and more likely to be engaged in invisible work, such as home-based or domestic and care work.
Recovery measures need to ensure immediate relief, but also point towards long-term solutions that contribute to the redistribution of wealth and new urban development, while also increasing resilience to the current and future pandemics or other disasters. There are tested measures that should be reemphasized.
Urban green recovery plans that include large-scale home renovation programs could ensure warm, healthy homes, and affordable energy bills for all. In the shorter-term, alleviation of payment defaults on the rents and utility bills of the energy poor should continue. In parallel, urban digital preparedness, more equal access to the virtual delivery of essential services, and provision of opportunities for virtual working and education for all in the future, need attention.
COVID-19 can be a wake up call to increase efforts to close the digital divide and push for structural change. The crisis has increased the urgency to redesign and improve informal settlements and provide adequate and efficient services that address the diverse needs of poor urban residents. This requires partnerships between urban municipalities, planners, and stakeholders, as well as strengthening local communities for inclusive planning strategies. More immediately, it is necessary to provide direct support to slum and informal settlement populations in terms of income support, adequate nutrition, energy, water, and other basic infrastructure and services.
 All in all, the COVID-19 pandemic has been a “test of societies, of governments, of communities, and of individuals”. Digital technologies, home renovation, and slum rehabilitation are the means, rather than the end to improve conditions for all, but if specifically targeted to the poor and most deprived, such measures can reduce inequalities and increase resilience.
All in all, the COVID-19 pandemic has been a “test of societies, of governments, of communities, and of individuals”. Digital technologies, home renovation, and slum rehabilitation are the means, rather than the end to improve conditions for all, but if specifically targeted to the poor and most deprived, such measures can reduce inequalities and increase resilience.
Reference:
Boza-Kiss, B., Pachauri, S., & Zimm, C. (2021). Deprivations and Inequities in Cities Viewed Through a Pandemic Lens. Frontiers in Sustainable Cities 3 e645914. [pure.iiasa.ac.at/17121]
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the Nexus blog, nor of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.


You must be logged in to post a comment.